To tylko jedna z 26 stron tej notatki. Zaloguj się aby zobaczyć ten dokument.
Zobacz
całą notatkę
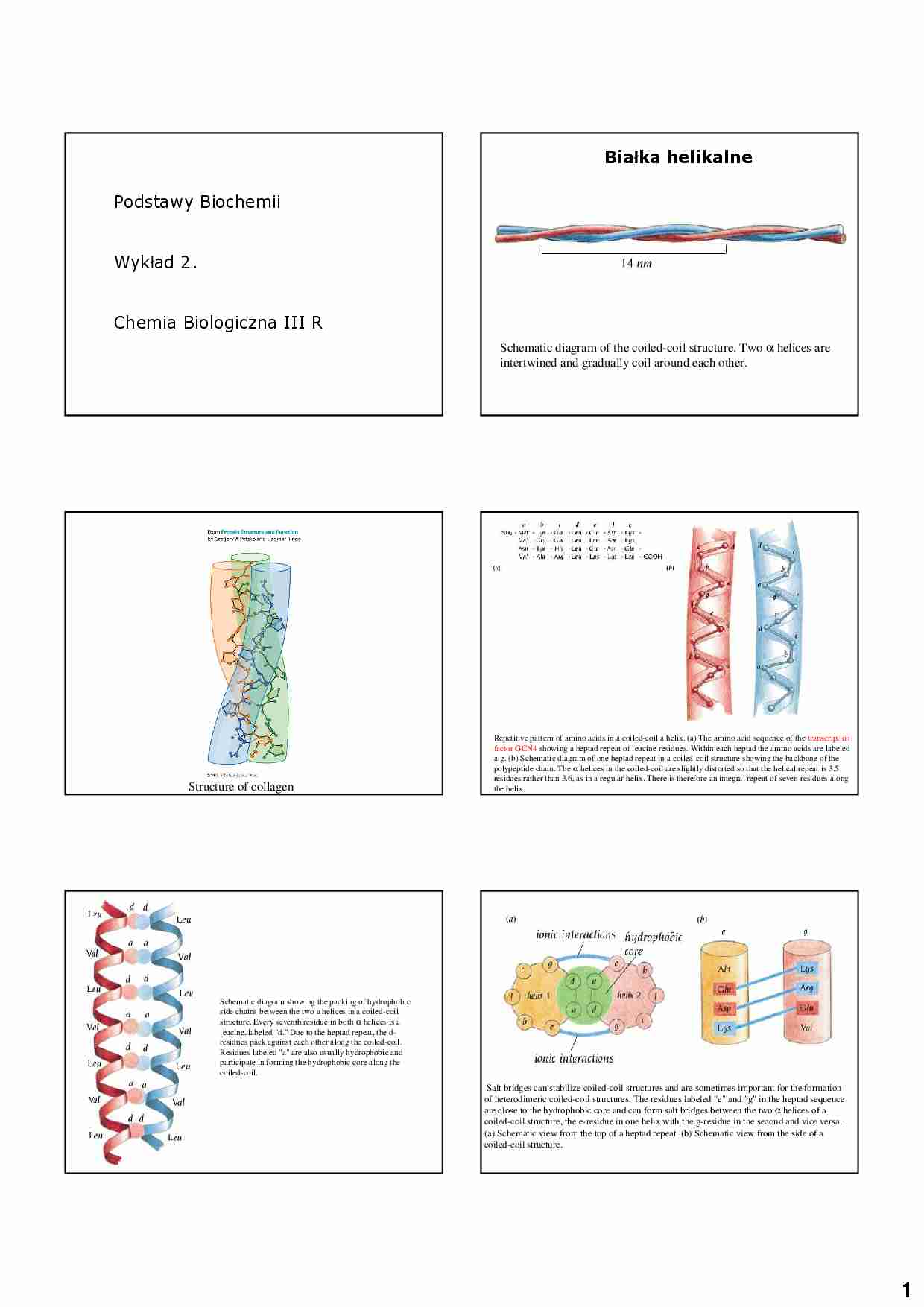
1 Podstawy Biochemii Wykład 2. Chemia Biologiczna III R Schematic diagram of the coiled-coil structure. Two α helices are intertwined and gradually coil around each other. Bia ł ka helikalne Structure of collagen Repetitive pattern of amino acids in a coiled-coil a helix. (a) The amino acid sequence of the transcription factor GCN4 showing a heptad repeat of leucine residues. Within each heptad the amino acids are labeled a-g. (b) Schematic diagram of one heptad repeat in a coiled-coil structure showing the backbone of the polypeptide chain. The α helices in the coiled-coil are slightly distorted so that the helical repeat is 3.5 residues rather than 3.6, as in a regular helix. There is therefore an integral repeat of seven residues along the helix. Schematic diagram showing the packing of hydrophobic side chains between the two a helices in a coiled-coil structure. Every seventh residue in both α helices is a leucine, labeled "d." Due to the heptad repeat, the d- residues pack against each other along the coiled-coil. Residues labeled "a" are also usually hydrophobic and participate in forming the hydrophobic core along the coiled-coil. Salt bridges can stabilize coiled-coil structures and are sometimes important for the formation of heterodimeric coiled-coil structures. The residues labeled "e" and "g" in the heptad sequence are close to the hydrophobic core and can form salt bridges between the two α helices of a coiled-coil structure, the e-residue in one helix with the g-residue in the second and vice versa. (a) Schematic view from the top of a heptad repeat. (b) Schematic view from the side of a coiled-coil structure. 2 Four-helix bundles frequently occur as domains in a proteins. The arrangement of the α helices is such that adjacent helices in the amino acid sequence are also adjacent in the three-dimensional structure. Some side chains from all four helices are buried in the middle of the bundle, where they form a hydrophobic core. (a) Schematic representation of the path of the polypeptide chain in a four-helix-bundle domain. Red cylinders are a helices. (b) Schematic view of a projection down the bundle axis. Large circles represent the main chain of the α helices; small circles are side chains. Green circles are the buried hydrophobic side chains; red circles are side chains that are exposed on the surface of the bundle, which are mainly hydrophilic. The polypeptide chains of cytochrome b562 and human growth hormone both form four-helix- bundle structures. In cytochrome b562 (a) adjacent helices are antiparallel, whereas the human
(…)
… 434 repressor fragment and a palindromic synthetic
14mer of DNA. The two binding sites of the repressor dimer to the DNA are identical. The
recognition helices of the repressor are red, and the first helix of the helix-turn-helix motif is
blue.
Schematic diagrams illustrating the complex between DNA (orange) and one monomer of the
homeodomain. The recognition helix (red) binds in the major groove of…
….
Monomer białka filamentu pośredniego ukazany w (A) składa się z centralnej pałeczkowej
domeny z globularnymi regionami na kaŜdym końcu. Pary monomerów łączą się tworząc
dimer (B), a dwa dimery zestawiają się następnie tworząc dachówkowato ułoŜony tetramer
(C).
11
Budowa filamentu pośredniego.
Budowa filamentu pośredniego.
Tetramery mogą upakowywać się razem koniec do końca, jak pokazano to w (D…
… extended as new knowledge is gained.
aktyna
12
Kinezyna i dyneina: silniki napędzane ATP, które przyczepiają się do organelli
i ciagną je wzdłuŜ mikrotubularnych „szyn”
organellum albo pęcherzyk
kinezyna
dyneina
mikrotubule
dimer tubuliny
Structural transformation in a serine protease inhibitor on binding protease
Ligand-induced conformational change
activates aspartate transcarbamoylase
Models for the…
… fashion.
Ribbon diagram
representations of the
structures of domain B1
from protein G (blue) and
the dimer of Rop (red).
The fold of B1 has been
converted to an α-helical
protein like Rop by
changing 50 % of its
amino acids sequence.
The hemoglobin molecule is built up of four polypeptide chains: two α chains and two β
chains. Each chain has a three-dimensional structure similar to that of myoglobin: the…
… a barrel, which is viewed along the barrel axis
in (b) and perpendicular to this axis in (c).
The binding site for retinol inside the RBP barrel is lined with hydrophobic residues. They
provide a hydrophobic surrounding for the hydrophobic part of the retinol molecule.
Schematic view down the fourfold axis of the tetrameric
neuraminidase
molecule of
Schematic diagram of the structure of human plasma…
… calcium atom is bound to one of the motifs in the muscle protein troponin-C through six oxygen
atoms: one each from the side chains of Asp (D) 9, Asn (N) 11, and Asp (D) 13; one from the main chain of
residue 15; and two from the side chain of Glu (E) 20. In addition, a water molecule (W) is bound to the
calcium atom. (c) Schematic diagram illustrating that the structure of troponin-C is built up from…
... zobacz całą notatkę






Komentarze użytkowników (0)